In the previous post, we used tf.keras to build and train a 2-layer neural network to predict digits 0-9 with MNIST dataset. This time, we will step up our game a bit when we build a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for our learning.
I - Load Packages and Define Constants
# Load packages
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(1)
# Define constants
NUMBER_OF_CLASSES = 10
EPOCHS = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 2**6
VALIDATION_SPLIT = .2
II - Load and Process the Dataset
1. Load data
# Load MNIST dataset
(X_train, Y_train), (X_test, Y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
print("X_train's shape:", X_train.shape)
print("Y_train's shape:", Y_train.shape)
print("X_test's shape:", X_test.shape)
print("Y_test's shape:", Y_test.shape)
X_train's shape: (60000, 28, 28)
Y_train's shape: (60000,)
X_test's shape: (10000, 28, 28)
Y_test's shape: (10000,)
2. Convert to the dataset to float32
print("Data type of X_train:", X_train.dtype)
print("Data type of X_test:", X_test.dtype)
Data type of X_train: uint8
Data type of X_test: uint8
X_train_preprocessed = X_train.astype('float32')
X_test_preprocessed = X_test.astype('float32')
print("Data type of X_train_preprocessed:", X_train_preprocessed.dtype)
print("Data type of X_test_preprocessed:", X_test_preprocessed.dtype)
Data type of X_train_preprocessed: float32
Data type of X_test_preprocessed: float32
2. Normalize the data
# Check range of values (peak to peak)
print("Peak-to-peak value of X_train:", np.ptp(X_train_preprocessed))
print("Peak-to-peak value of X_test:", np.ptp(X_test_preprocessed))
Peak-to-peak value of X_train: 255.0
Peak-to-peak value of X_test: 255.0
# Normalize to range (0-1)
X_train_preprocessed = np.divide(X_train_preprocessed, 255)
X_test_preprocessed = np.divide(X_test_preprocessed, 255)
print("Peak-to-peak value of X_train:", np.ptp(X_train_preprocessed))
print("Peak-to-peak value of X_test:", np.ptp(X_test_preprocessed))
Peak-to-peak value of X_train: 1.0
Peak-to-peak value of X_test: 1.0
3. Reshape training and target variables
# One-hot encode for Y_train and Y_test
Y_train_preprocessed = keras.utils.to_categorical(Y_train, NUMBER_OF_CLASSES)
Y_test_preprocessed = keras.utils.to_categorical(Y_test, NUMBER_OF_CLASSES)
print("Y_train_preprocessed's shape:", Y_train_preprocessed.shape)
print("Y_test_preprocessed's shape: ", Y_test_preprocessed.shape)
Y_train_preprocessed's shape: (60000, 10)
Y_test_preprocessed's shape: (10000, 10)
# Reshape X_train_preprocessed, X_test_preprocessed
X_train_preprocessed = X_train_preprocessed.reshape(X_train_preprocessed.shape[0],
X_train_preprocessed.shape[1],
X_train_preprocessed.shape[2],
1) # 1 represents 1 channel
X_test_preprocessed = X_test_preprocessed.reshape(X_test_preprocessed.shape[0],
X_test_preprocessed.shape[1],
X_test_preprocessed.shape[2],
1) # 1 represents 1 channel
III - Build a Convolutional Model
In this post, we will build a CNN to solve MNIST. Specifically we will use one of the earliest CNN architecture called LeNet-5 for our problem. Basically, LeNet-5 consists of seven layers, which are as follows:
Conv2D: 6 filters 5x5, stride = 1, padding = 2.AveragePooling2D: 2x2, stride = 2, padding = 0.Conv2D: 16 filters 5x5, stride = 1, padding = 0.AveragePooling2D: 2x2, stride = 2, padding = 0.Dense: 120 units, activation = “relu”.Dense: 84 units, activation = “relu”.Dense: 10 units, activation = “softmax”.
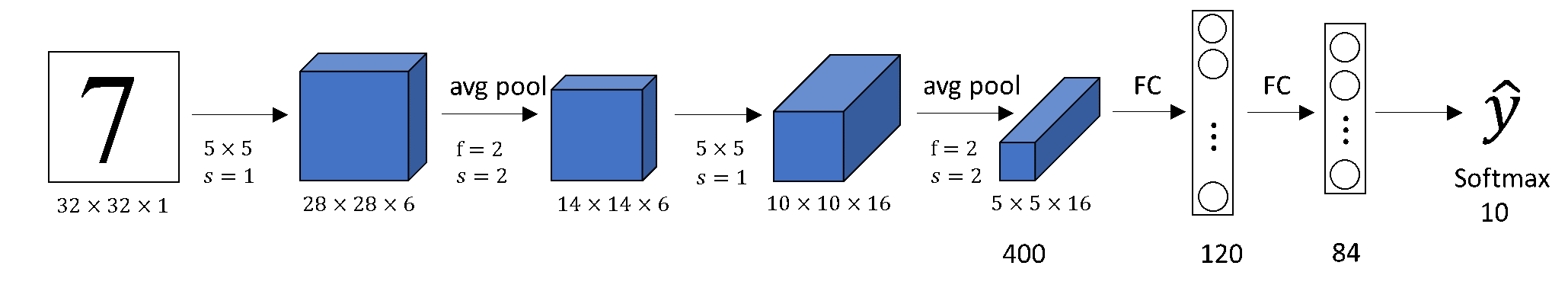
mnist_model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)),
keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D(padding=(2, 2)),
keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=6, kernel_size=(5, 5), strides=1, padding="valid"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Activation("relu"),
keras.layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding="valid"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=(5, 5), padding="valid"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Activation("relu"),
keras.layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), padding="valid"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(units=120, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Dense(units=84, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.Dense(units=10, activation="softmax")
])
# Model summary
mnist_model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
zero_padding2d (ZeroPadding2 (None, 32, 32, 1) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 6) 156
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization (BatchNo (None, 28, 28, 6) 24
_________________________________________________________________
activation (Activation) (None, 28, 28, 6) 0
_________________________________________________________________
average_pooling2d (AveragePo (None, 14, 14, 6) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_1 (Batch (None, 14, 14, 6) 24
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 10, 10, 16) 2416
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_2 (Batch (None, 10, 10, 16) 64
_________________________________________________________________
activation_1 (Activation) (None, 10, 10, 16) 0
_________________________________________________________________
average_pooling2d_1 (Average (None, 5, 5, 16) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_3 (Batch (None, 5, 5, 16) 64
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 400) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 120) 48120
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_4 (Batch (None, 120) 480
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 84) 10164
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_5 (Batch (None, 84) 336
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 10) 850
=================================================================
Total params: 62,698
Trainable params: 62,202
Non-trainable params: 496
_________________________________________________________________
# Compile our model
mnist_model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Fit the model
history = mnist_model.fit(X_train_preprocessed,
Y_train_preprocessed,
epochs=EPOCHS,
verbose=0,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
validation_split=VALIDATION_SPLIT)
# Evaluate the new model using a test set
mnist_model.evaluate(X_test_preprocessed, Y_test_preprocessed)
313/313 [==============================] - 1s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0417 - accuracy: 0.9926
[0.041718218475580215, 0.9926000237464905]
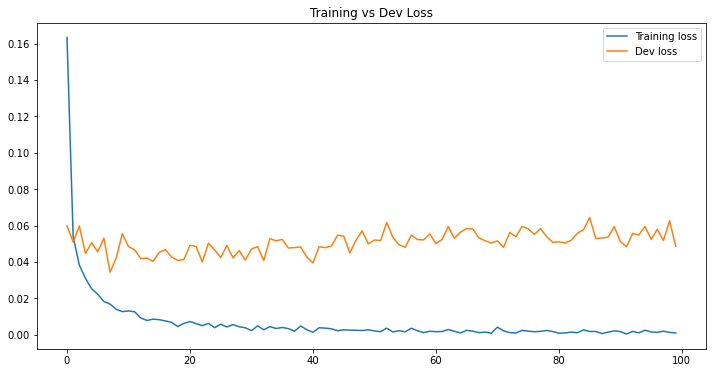
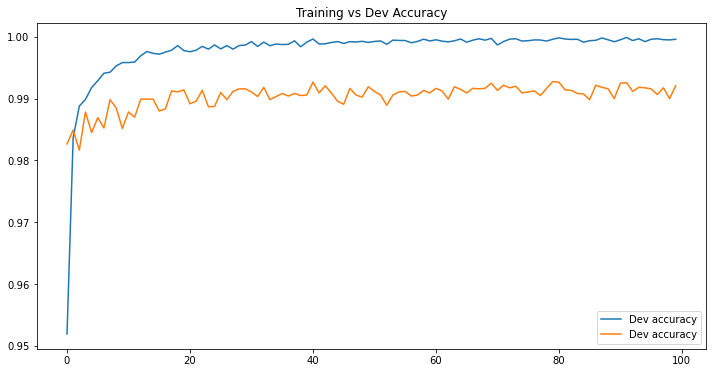
IV - Model History
df_loss_acc = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
df_loss_acc.describe()
| loss | accuracy | val_loss | val_accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 100.000000 | 100.000000 | 100.000000 | 100.000000 |
| mean | 0.006823 | 0.997854 | 0.050759 | 0.990359 |
| std | 0.017671 | 0.005248 | 0.005864 | 0.002038 |
| min | 0.000413 | 0.951917 | 0.034314 | 0.981667 |
| 25% | 0.001712 | 0.998427 | 0.047801 | 0.989917 |
| 50% | 0.002462 | 0.999198 | 0.051356 | 0.990917 |
| 75% | 0.004907 | 0.999464 | 0.054700 | 0.991583 |
| max | 0.163319 | 0.999896 | 0.064379 | 0.992750 |
# Make two corresponding data frames from history df.
df_loss = df_loss_acc[['loss', 'val_loss']]
df_loss = df_loss.rename(columns={'loss': 'Training loss', 'val_loss': 'Dev loss'})
df_acc = df_loss_acc[['accuracy', 'val_accuracy']]
df_acc = df_acc.rename(columns={'accuracy': 'Dev accuracy', 'val_accuracy': 'Dev accuracy'})
# Plot two data frames
df_loss.plot(title='Training vs Dev Loss', figsize=(12, 6))
df_acc.plot(title='Training vs Dev Accuracy', figsize=(12, 6))
<AxesSubplot:title={'center':'Training vs Dev Accuracy'}>
V - Conclusion
In this post, we built a LeNet-5 CNN to recognize digits with MNIST dataset. In comparison to the previous post, this time, our model achieved a much better prediction accuracy on a seperate test set with 99.26% (vs. 96.66%).